What is Parkinson’s Disease?

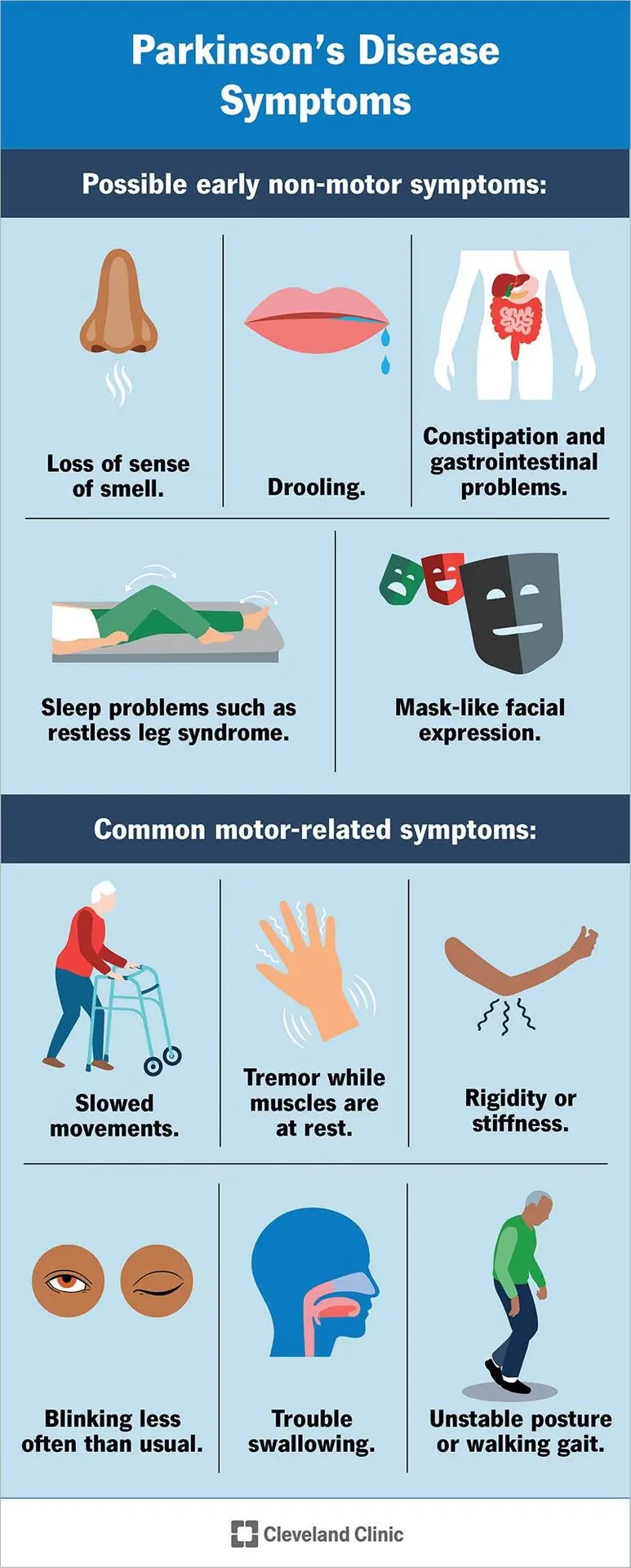
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions worldwide, leading to a wide range of motor and non-motor symptoms. Early recognition of these symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and improving quality of life. Patients may experience tremors, muscle rigidity, slow movement (bradykinesia), balance issues, and speech difficulties, which can gradually become more severe as the disease advances.
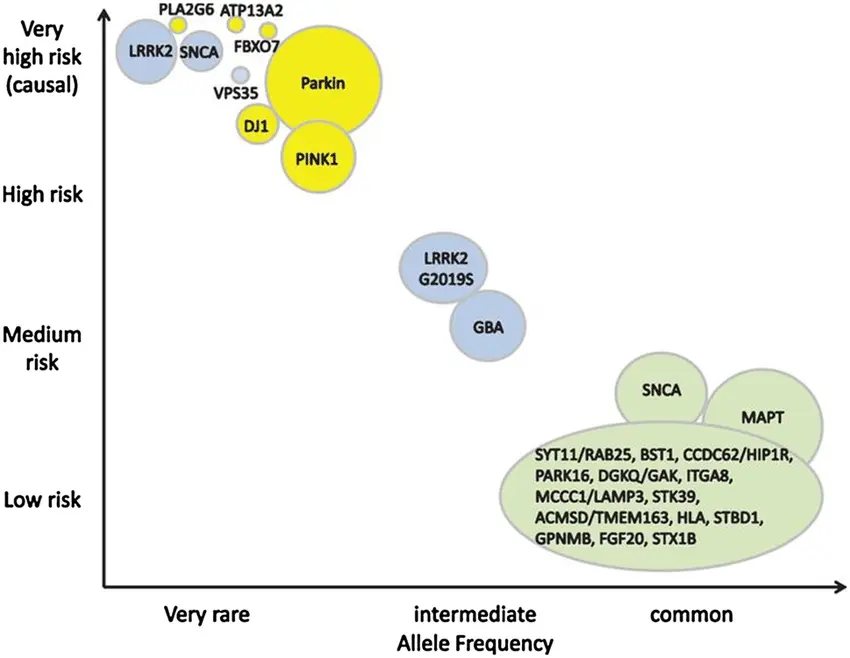
Causes and Risk Factors of Parkinson’s Disease
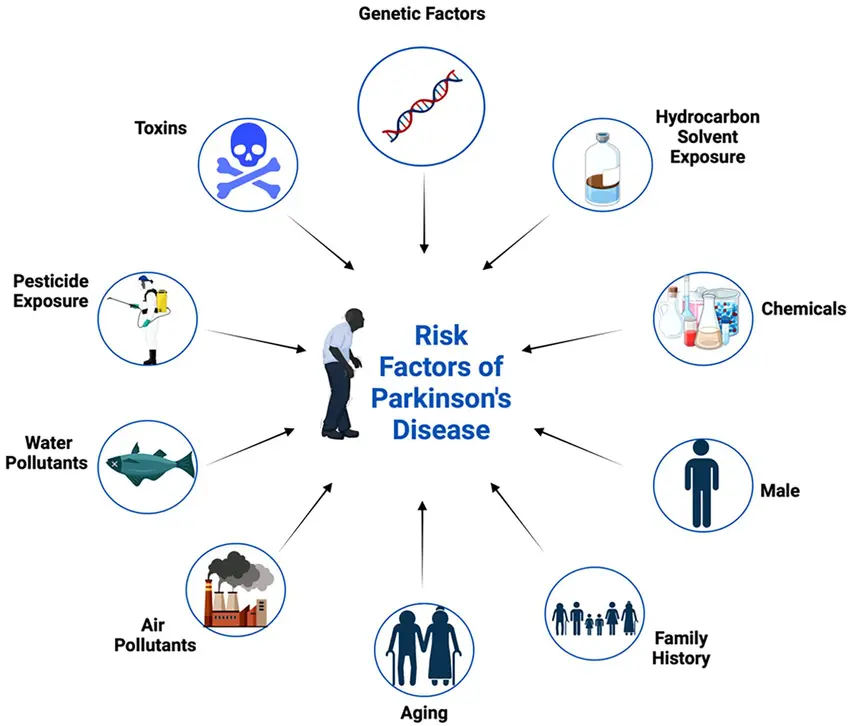
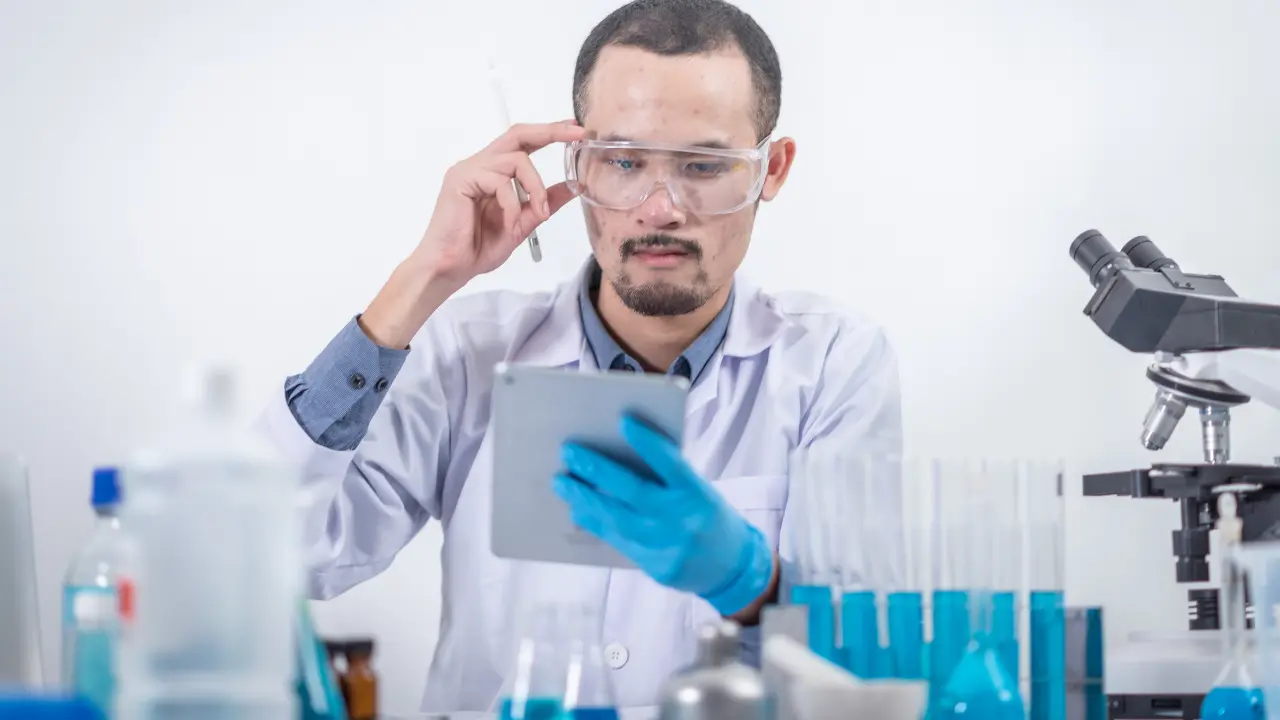
Early and accurate diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is essential for effective management and treatment. Detecting the disease in its initial stages allows patients to benefit from therapies that slow progression, improve symptoms, and enhance quality of life. Parkinson’s is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluations, medical imaging, and specialized tests that assess both motor and non-motor symptoms.
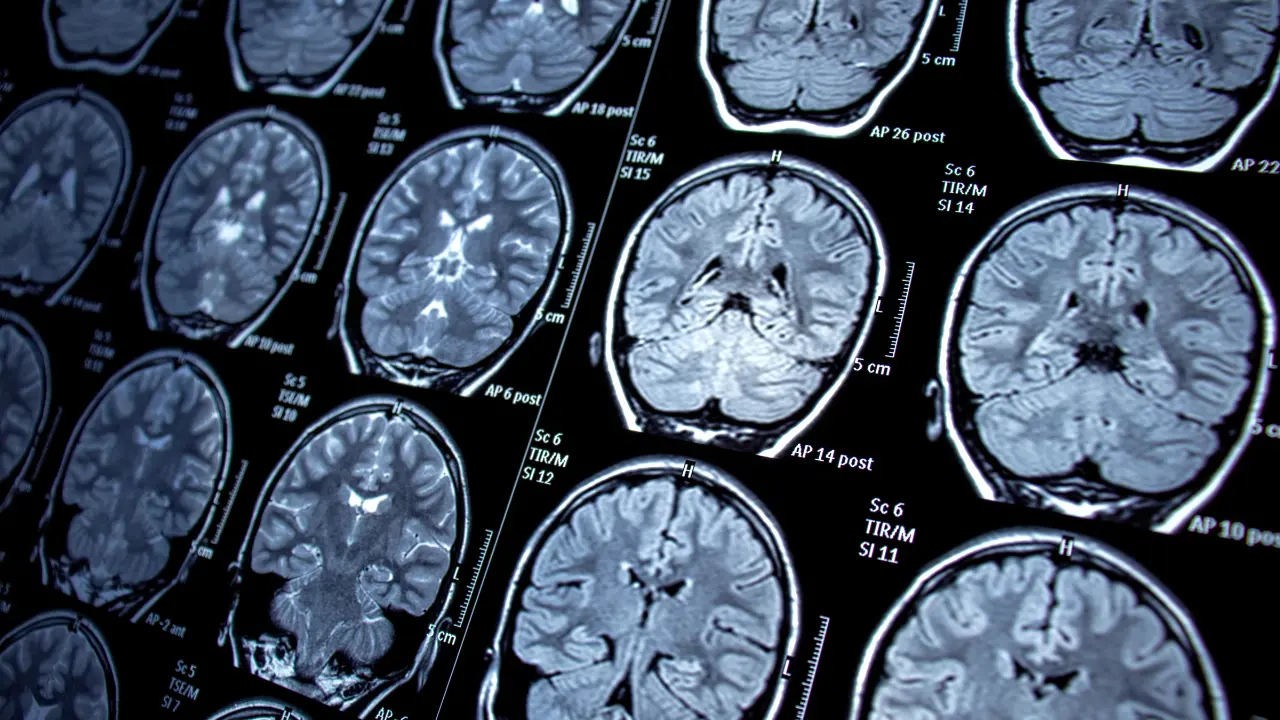
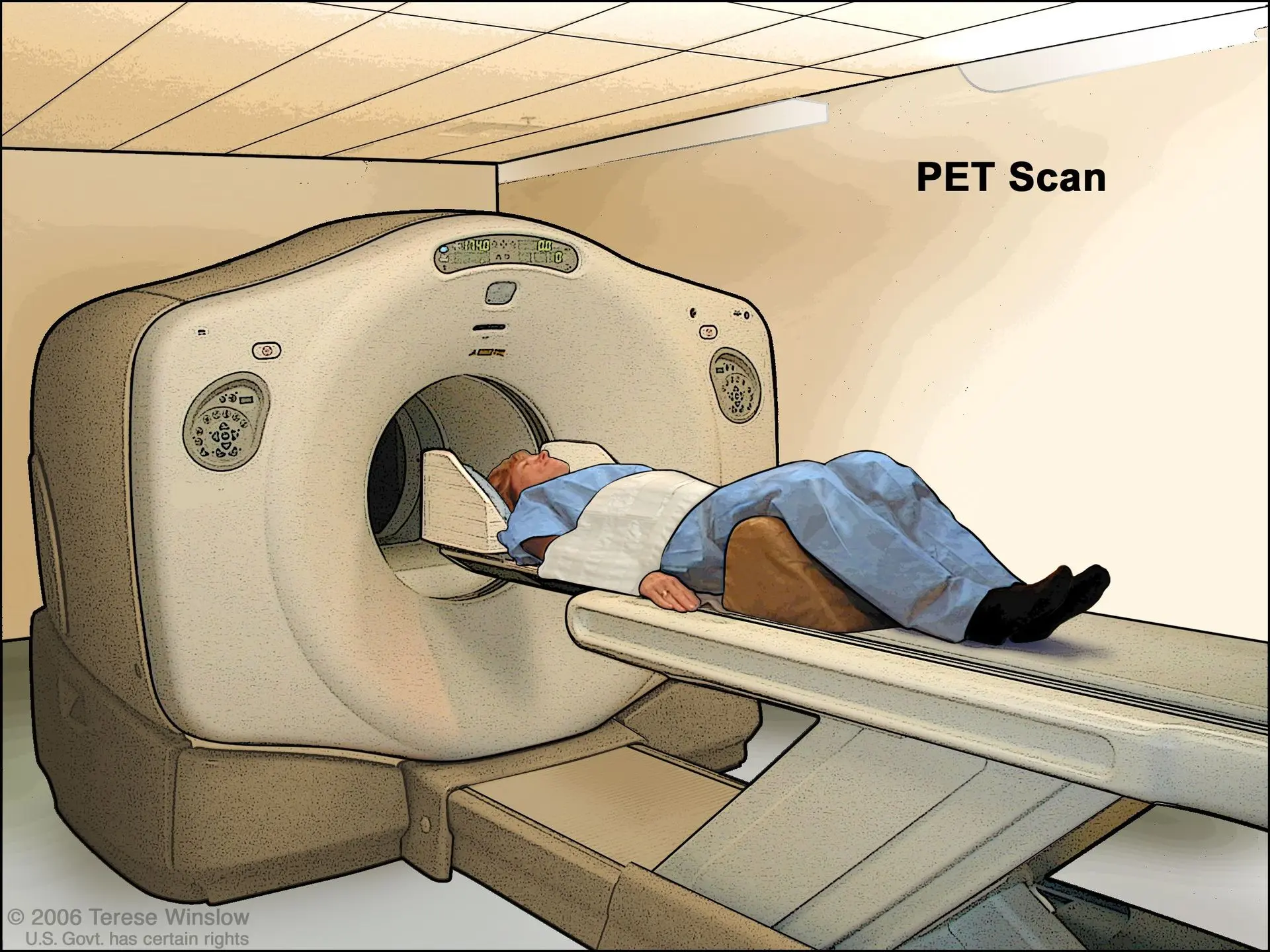
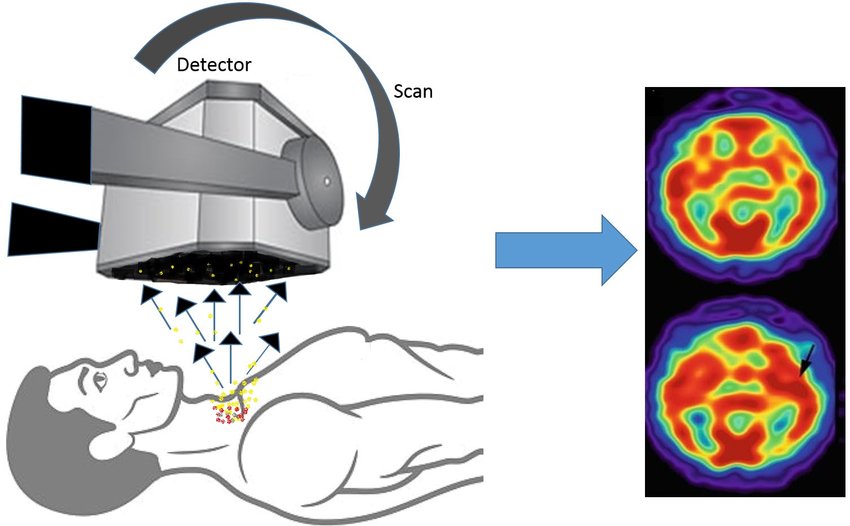
Medical Imaging Techniques
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Detects structural changes in the brain and rules out other conditions
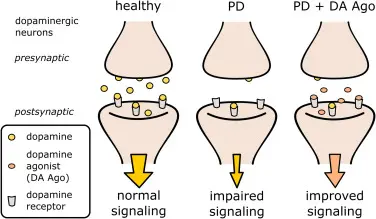
- DaTscan: Specialized imaging to visualize dopamine transporter levels in the brain, highlighting dopamine deficiency
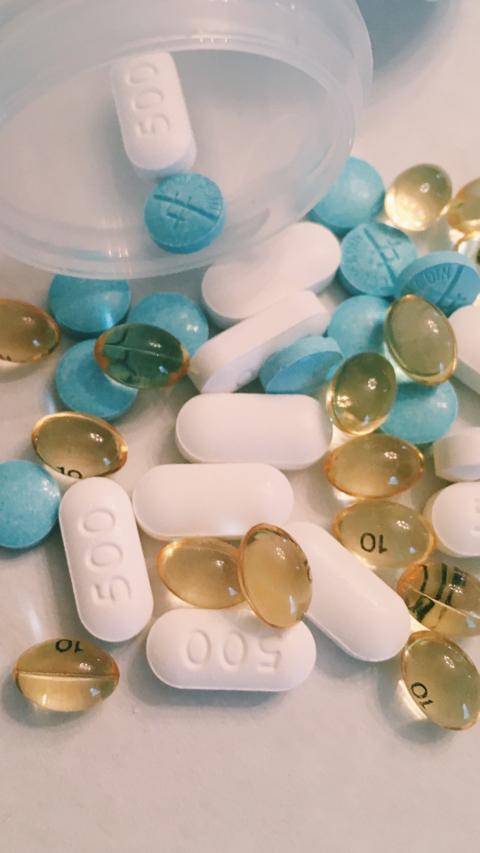
While there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease, a range of traditional treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Early and effective treatment can reduce motor and non-motor symptoms, enhance daily functioning, and slow disease progression. These therapies include medications, surgical options, and supportive care, which are tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Many patients and caregivers have questions about Parkinson’s disease. Here are answers to some of the most commonly asked questions, providing clear, reliable information for those affected.
Currently, there is no cure, but treatments can manage symptoms, slow progression, and improve quality of life.
Early signs often include mild tremors, stiffness, slow movements (bradykinesia), and subtle changes in handwriting or balance.
While medications are essential, lifestyle approaches like regular exercise, balanced diet, physiotherapy, stress management, and sufficient sleep can complement treatment.