Introduction:
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) research has expanded rapidly in recent years, focusing on early diagnosis, biomarker discovery, and understanding the underlying mechanisms of neurodegeneration. Advancements in laboratory instruments, molecular biology techniques, and neuroimaging have revolutionized the way Parkinson’s is detected and monitored, providing researchers and clinicians with unprecedented precision.
Modern Detection Methods:
-
Biochemical Analysis:
- Protein Biomarkers: Proteins such as α-synuclein, tau, and DJ-1 are critical for PD research. Misfolded α-synuclein aggregates are a key pathological hallmark. Read more
- Techniques: ELISA provides quantitative analysis, Western blot identifies specific protein isoforms, and Mass Spectrometry offers high-precision profiling.
- Applications: Enables early detection and monitoring of disease progression in clinical trials and laboratory studies.
-
Imaging Techniques:
- MRI/fMRI: Detect structural and functional changes in the brain. Functional MRI can track brain activity during motor tasks.
- PET/SPECT: Visualize dopaminergic neuron activity using radioactive tracers, allowing early detection of neuron degeneration before significant clinical symptoms appear.
- CT Scans: Used primarily to exclude other neurological disorders.
-
Electrophysiological Techniques:
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Monitors neural activity and can help study motor and cognitive dysfunctions.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures muscle activity and helps evaluate tremors and rigidity in PD patients.
Laboratory Instruments and Reagents:
- ELISA Microplate Readers: Quantify biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid or blood.
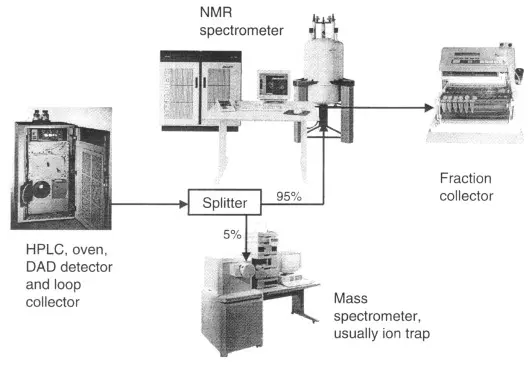
- HPLC and Mass Spectrometry: Measure neurotransmitter levels and protein profiles.Read more
- MRI, PET, and SPECT Scanners: Provide high-resolution imaging of the brain’s structure and function.
- Reagents: Include antibodies, enzyme substrates, buffers, and radioactive tracers for imaging.For more information click here
- Genetic Sequencers: Detect mutations that increase PD susceptibility.
Innovations in Research:
- Development of ultrasensitive biomarker assays allows detection of early-stage PD.
- Machine learning and AI algorithms analyze imaging and molecular data for precise diagnosis.
- Neuroprotective and disease-modifying therapies are under investigation, relying on accurate biomarker and imaging data for evaluation.
Conclusion:
Innovative laboratory instruments and detection techniques are transforming Parkinson’s Disease research. From biochemical analysis to advanced imaging, these tools provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms and enable early diagnosis. As research progresses, continued innovation will pave the way for more effective treatments and improved patient outcomes.